ECO 201 SNHU Memorandum Report Identifies
Description
Competencies
In this project, you will demonstrate your mastery of the following competencies:
- Inform business decisions using microeconomic models and theories
- Determine the impact of economic costs on organizational and individual decision making
- Explain how market structure impacts a businesss entry and exit into a market and its ability to generate economic profit
Scenario
You and your friend from college have just graduated. You majored in business, and your friend majored in a creative field. Your friend is highly inventive and has come up with an excellent idea for a new product. You both believe in this idea so much that you have agreed to become business partners. However, before you embark on your entrepreneurial adventure, you will have to explain some key microeconomics concepts to your partner that are important to make sound business decisions.
Your business partner is less than enthusiastic about this prospect and has never had an interest in what is often described as the dry and boring field of economics. Every time you have tried to engage your partner in practical discussions, they brush you off and decide to go play video games instead.
Aha! This gives you an idea: What if you could convince your friend to learn about economics through games? You have found several simulation games that demonstrate in real and interesting ways the economic principles that you know your partner needs.
Once you have played the games, you will create a memorandum report summarizing for your friend the educational value of your experiment. In your memorandum, you will restate the key principles and takeaways of each simulation, as well as illustrate how these ideas are relevant to your future entrepreneurial success.
Directions
First, assemble the materials that you will need to complete this assignment:
- You will need several simulation report images for your memorandum. All the necessary data visualizations will be generated after you have completed each simulation game. You will be required to save image files of your simulation reports for your simulation discussions. These should also be used to create your memorandum report for the course project. If you have any questions or concerns about the simulation data that should be used for your project, you should promptly reach out to your instructor.
- Review and use the Project Template located in the What to Submit section.
You are expected to reference any source material used in your memorandum report with appropriate citations. To support you, a References page has been added to the project template with a citation for this courses reading already provided. Any other references you add should be cited according to APA format.
Once you have assembled the required materials listed above, you can now begin drafting your memorandum report by completing the following steps:
- Comparative Advantage: Discuss the Comparative Advantage (With Trade) simulation that you played in Module Two. You should add the Production Decisions graph and the Production Trade graph (i.e., the graph showing how many hamburgers per fries) from you simulation report into the project template as Figures 1.1 and 1.2. Then, answer the following questions in the paragraphs below the figures:
- How does this simulation demonstrate how individuals evaluate opportunity costs to make business decisions? Use the Production Decisions graph from the simulation as a reference to explain what role the production-possibility frontier (PPF) has in the decision-making process.
- Explain how comparative advantage impacts a firms decision to engage in trade. Would a businesss decision to trade cause a change to its PPF? Provide specific reasoning to support your claims.
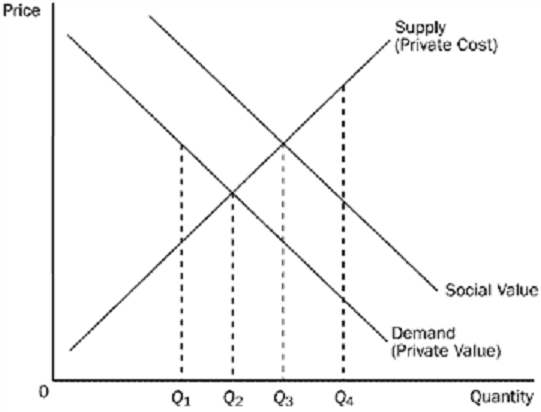
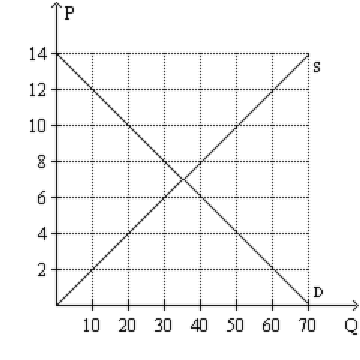
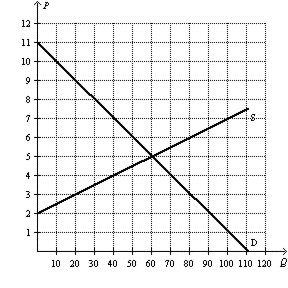
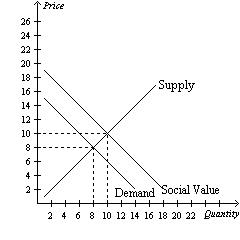
- Competitive Markets and Externalities: Discuss the Competitive Markets and Externalities simulations (both with and without policy interventions) that you played in Modules Three and Four. Add the Supply and Demand chart and the Outcomes by Market table from your simulation reports into the project template as Figures 2.1 and 2.2. Then, answer the following questions in the paragraphs below the figures:
- What impact do policy interventions have on the supply and demand equilibrium for a product? Provide specific examples from the simulation to illustrate.
- What are the determinants of price elasticity of demand? Identify at least three examples. Based on the outcome of the simulation, explain how price elasticity can impact pricing decisions and total revenue of the firm.
- Based on the results of the simulation, can policy market interventions cause consumer or producer surplus? Explain why using specific reasoning.
- Production, Entry, and Exit: Discuss the Production, Entry, and Exit simulation that you played in Module Five. Add the Aggregate Outcomes chart from your simulation report into the project template as Figure 3.1. Then, answer the following questions in the paragraphs below the figure:
- Analyze a business owners decision making regarding whether to enter a market. For example, what factors determined the drivers market entry and exit in the simulation? Use economic models to support your analysis.
- How does a business owner applying the concept of marginal costs decide how much to produce? For example, how did the driver determine how many hours to drive each day? Use economic models to explain.
- How does the impact of fixed costs change production decisions in the short run and in the long run? Use the average-total-cost (ATC) model included in the module reading chapters to demonstrate this impact.
- Market Structures: Discuss the market structures simulations (Price Discrimination and Cournot) that you played in Modules Six and Seven. Then, do the following in the project template:
- Complete Table 4.1 as a reference guide for your business partner. The table should compare the attributes of each of the four listed market structures.
- Answer the following questions in the paragraphs below the table:
- Explain what market inefficiencies derive from monopolies and monopolistic competition. Use examples from the textbook to support your claims.
- How do firms in an oligopolistic market set their prices? Use specific examples from the simulations or from the textbook to support your claims.
- Explain how firms that compete in the four different market structures determine profitability. Use specific examples from the simulations or the textbook to support your claims.
- Conclusions: Draw your overall conclusions about the relevance and significance of microeconomics. How will microeconomics principles impact your business decisions moving forward? Provide recommendations to your business partner for your future business venture.
- Finally, ensure that all of your sources are properly cited using in-line citations and references according to APA format.
What to Submit
To complete this project, you must submit the following:
Memorandum Report
Your memorandum report should summarize the key principles and takeaways of each microeconomics simulation for your business partner. It should also illustrate how these ideas are relevant to your future entrepreneurial success.
Template: Project Template Word Document
Use this template to structure your memorandum report, and submit it as a Word document. Sources should be cited according to APA style.
Supporting Materials
The following resources support your work on the project:
Video: How to Use the Snipping Tool (Beginners Guide) (for PC) (5:23)
Use this tutorial for help with snipping, copying, and pasting your data visualizations into your project template.
A captioned version of this video is available: How to Use the Snipping Tool (Beginners Guide) (CC) Video.
Resource: Is There a Snipping Tool for Mac?
Use this tutorial for help with snipping, copying, and pasting your data visualizations into your project template.
Resource: APA Style Basics
Use this resource to support your in-line citations and full references in the References section of your project template.